Peristaltic Pumps
78% lighter weight, more efficient and more compact.
Peristaltic pumps are a type of positive displacement pump used for pumping a variety of fluids. The fluid is contained within a flexible tube fitted inside a circular pump housing. A rotor with a number of rollers compresses the flexible tube. As the rotor turns, the part of the tube under compression is pinched closed thus forcing the fluid to move through the tube.
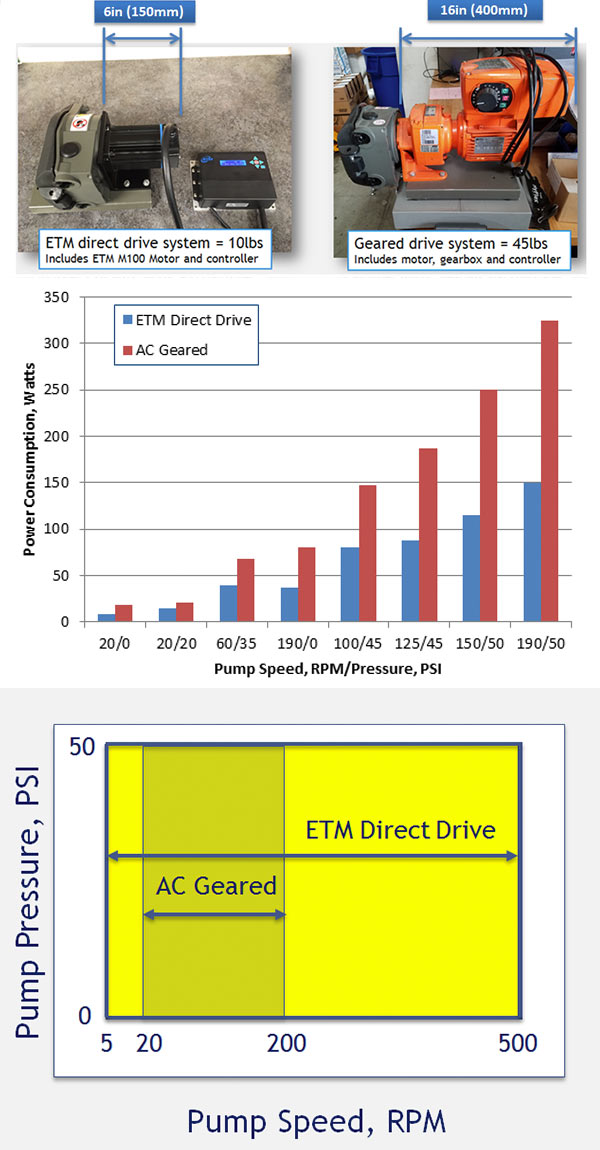
Peristaltic pumps require relatively high torque at low rotational speeds, typically in the range of 5 to 500 RPM, well below the direct drive capability for conventional AC or DC motors. As a result, conventional motors are operated at a higher speed (over 1000 rpm) and a speed reduction gearbox is necessary to achieve the required torque and rotational speed. These geared drive systems are large, heavy, inefficient and the gearbox increases cost while causing a reliability and maintenance burden.

 Precision Conveyors
Precision Conveyors